Veranstaltungen und Aktivitäten
How Can We Explain the Lag of Japan’s Sharing Economy?
In recent years, the emergence of “sharing economy” has brought people plenty of conveniences to collaboratively make use of under-utilized inventory through fee-based sharing. The topic of the sharing economy has also caught attention in public and academic debate. According to Yano Institute, the size of the Japanese sharing economy by transaction is 0.64 billion USD in 2017 and is estimated to reach only about 1.24 billion USD by 2022, which is relatively weak compared with other developed countries and even some developing countries. The Japanese Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications also states that the size of Japan’s sharing economy is relatively small. This research tries to seek answers to the question of why Japan’s sharing economy has evolved relatively slowly. Because there is no existing theory to explain the lag of Japan’s sharing economy, this research regards the sharing economy as a new form of process innovation that creates a new way for people to get access to goods and services. Taking a macro perspective theoretically informed by the National Systems of Innovation (NSI) literature, this research adopts semi-structured interviews to acquire in-depth insights from industry insiders.
Speaker:
Junxi Yao, University of Sheffield
Protecting Children in Family Separation
As Japan has the sole custody system after divorce, there are a number of parental disputes over child custody and visitation or access nowadays. Currently, only 1/3 of children with divorced parents can have access to their non-custodial parent, and only 1/4 of children obtain child support from their non-custodial parent. In contrast, Germany and other Western countries have implemented joint custody after divorce, which requires both parents to consult with each other and take joint decisions in relation to long-term issues concerning their children.
The divergent legal settings and societal conditions between Japan and Western countries yield difficult questions in a cross-border family separation. Prof. Nishitani will address the historical, legal and societal background of these differences in family law institutions between Japan and Western countries with a particular focus on Germany. Prof. Odagiri will show what we have learned about the impact of divorce on children from research in psychology and what actions are now being taken.
Speakers:
Yuko Nishitani, Kyoto University
Noriko Odagiri, Tokyo International University
Autonomy, Belonging and Long-Distance Relationships in Europe and Japan
Individualization and mobility increasingly define romantic relationships. ‘Despatialization’ and internationalization of work and education have intensified tensions between occupation and relationships. Therefore, as couples negotiate and coordinate their lives, flexibility and agency become more necessary to sustain relationships. Decisions along the life course demand privileging either individual autonomy or dyadic belonging. As all options likely imply trade-offs, actors will try to balance autonomy and belonging. This is for example the case in long-distance relationships (LDR), which can be seen as ‘solutions’ to systemic challenges, that, however, cause new challenges. Against this background, my talk asks how long-distance couples ‘manage’ distance, belonging and their life courses.
Speaker
Markus Klingel, Bremen International Graduate School of Social Sciences
Regulating for a Better Work-life Balance: German and Japanese Experiences
Germany and Japan have experienced rapid growth in non-standard employment and particular in part-time work in the last 30 years. Nevertheless, both countries differ considerably when it comes to important indicators of work-life balance such as working time. According to the OECD, in Japan around 22 per cent of workers have a work week of 50 hours or more, whereas in Germany this applies to less than 5 per cent. Annual average working hours in Japan stand at 1,600 hours but only at about 1,300 in Germany. Despite these differences, in both countries policies that aim at more flexible working time regimes, including measures to reduce working hours, are currently high on the political agenda.
At this DIJ Forum we ask how the differences between the two countries can be explained and to what extent current debates are comparable.
Speakers:
Hartmut Seifert, WSI Düsseldorf
Katsutoshi Kezuka, Chuo University
Gemeinsame Bücherausstellung:
Nō und Kyōgen
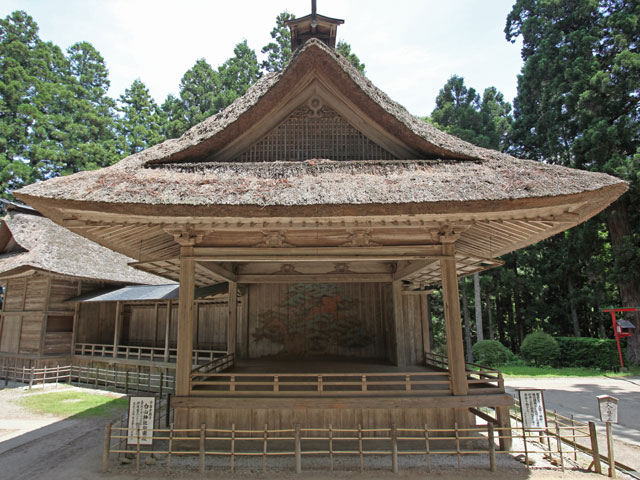 Wie wird die klassische japanische Bühnenkunst im Ausland gesehen und welche Forschung gibt es dazu?
Wie wird die klassische japanische Bühnenkunst im Ausland gesehen und welche Forschung gibt es dazu?
Die International House of Japan Library, die Bibliothèque de la Maison franco-japonaise sowie die Bibliothek des Deutschen Instituts für Japanstudien geben im Rahmen einer gemeinsamen Bücherausstellung Einblicke in englisch-, französisch- und deutschsprachige Übersetzungen sowie Forschungsliteratur zum Thema Nō und Kyōgen.
Falls Sie Fragen zu Inhalten oder zum Besuch der Ausstellung haben sollten, kontaktieren Sie bitte die jeweilige Bibliothek.
Writing (in) Iwate: Exploring a Local Literary Scene and its Fiction
The literary scene in Japan has one strong focal point: Tokyo. From the early 20th century onwards, publishers gathered in the capital, attracting those who aspired to be professional writers from all over the country. Still today, more than 76 percent of all Japanese publishing houses are located in Tokyo according to a recent report of the Japan Book Publishers Association. However, the situation for writers in other regions of Japan seems to have changed significantly as my research on literature in the prefecture of Iwate shows: While my study began with the question whether there was any local literary production in present-day Iwate at all, an on-site exploration yielded that a considerable literary scene actually does exist. Yet, this local literature is mostly overlooked by academia and media. To change this and draw attention to the literary production of Iwate, I dedicated my dissertation to the question what the local literary scene in Iwate and its literature look like.
In the presentation the focus will be put on the literary magazine Kita no bungaku [Literature of the North], which I identified as one of the key institutions supporting literature in Iwate.
Speaker:
Tamara Kamerer, University of Vienna
Report on the Transregional Academy „Infrastructures, Regions and Urbanizations“
The Berlin-based Forum Transregionale Studien and the Max Weber Stiftung – Deutsche Geisteswissenschaftliche Institute im Ausland had invited 18 doctoral and postdoctoral scholars from the humanities and social sciences to attend a Transregional Academy convened at the National University of Singapore (NUS) on the topic of “Infrastructures, Regions and Urbanizations”. The Academy was chaired by Weiqiang Lin and James D. Sidaway (National University of Singapore), Franz Waldenberger (Deutsches Institut für Japanstudien, Tokyo) and Simone Lässig (Deutsches Historisches Institut Washington). It was arranged in cooperation with the Asia Research Institute and its director Jonathan Rigg as well as the Max Weber Foundation Research Group on Borders, Mobility and New Infrastructures at NUS.
Read the full report by Franz Waldenberger
What Happens Abroad Stays Abroad? Expatriates’ Psychological Contracts
With multinational companies being globally active, deploying people in different locations all over the world has become a common practice. A recent survey of KMPG predicts that the number of international assignments will continue to increase in the next 5 years and that companies worldwide will continue to take advantage of their global workforce. Japanese multinational companies also strongly rely on this workforce as it enables them to control their foreign subsidiaries, foster knowledge transfer across national borders and establish globally standardized policies. According to the statistics of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the number of Japanese nationals working overseas increased by nearly 10% in the last five years. For FY 2017, 463,700 nationals were working for private enterprises abroad. Considering the crucial importance of these employees for the long-term corporate success, it becomes imperative for both researchers and practitioners alike to understand what determines expatriates´ success abroad and how human resource management practices may support expatriates to stay committed to their employers.
Speaker:
Tassilo Schuster, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München








 Open Access
Open Access 
